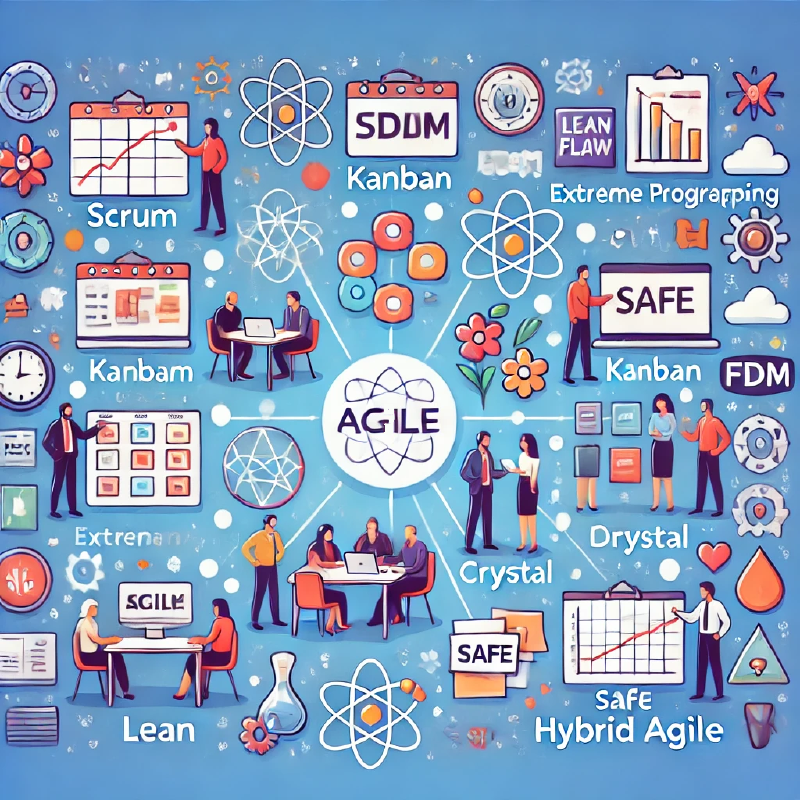
| Type | Description | Best For | Homepage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scrum | Structured framework with time-boxed sprints and defined roles. | Teams needing a structured, iterative approach. | Scrum.org |
| Kanban | Visual workflow management with continuous delivery and WIP limits. | Teams seeking flexibility and improved flow. | Kanban University |
| Extreme Programming (XP) | Focuses on technical excellence with practices like TDD and pair programming. | Software teams prioritizing high-quality code. | ExtremeProgramming.org |
| Lean | Optimizes efficiency by eliminating waste and maximizing value delivery. | Teams aiming for value optimization and waste reduction. | Lean Enterprise Institute |
| Crystal | Lightweight, customizable methodology emphasizing simplicity and communication. | Teams needing a tailored, minimalistic approach. | CrystalMethodologies.org |
| Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM) | Business-focused Agile framework with strict time and budget constraints. | Teams working on business-critical projects. | Agile Business Consortium |
| Feature-Driven Development (FDD) | Model-driven process focusing on iterative feature delivery. | Large-scale software projects. | FeatureDrivenDevelopment.com |
| Agile Unified Process (AUP) | Simplified version of RUP adapted to Agile practices. | Teams balancing Agile with structured processes. | Agile Unified Process |
| SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) | Framework for scaling Agile across large organizations. | Enterprises coordinating multiple Agile teams. | Scaled Agile Framework |
| Hybrid Agile | Combination of Agile and traditional methods (e.g., Waterfall). | Organizations transitioning to Agile or with mixed project needs. | N/A |
Comparing Agile Frameworks and Methodologies
1. Scrum
Overview: Scrum is a structured Agile framework emphasizing iterative progress through fixed-length sprints (usually 2-4 weeks). It defines roles such as Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team to foster accountability and collaboration.
Best For: Teams that need a structured, time-boxed approach.
Key Strengths:
Clearly defined roles and responsibilities.
Regular sprint reviews and retrospectives ensure continuous improvement.
Challenges:
- Less flexible during a sprint, as tasks are locked in.
2. Kanban
Overview: Kanban is a visual workflow management system focused on continuous delivery and minimizing work in progress (WIP). Teams pull tasks through stages as capacity allows.
Best For: Teams seeking flexibility and improved flow without fixed iterations.
Key Strengths:
Highly visual and flexible.
Encourages incremental improvements.
Challenges:
- Lack of fixed deadlines can be an issue for time-sensitive projects.
3. Extreme Programming (XP)
Overview: XP focuses on technical excellence in software development, emphasizing practices like Test-Driven Development (TDD), Pair Programming, and Continuous Integration.
Best For: Software development teams prioritizing high-quality code.
Key Strengths:
Ensures robust, maintainable code.
High levels of customer involvement.
Challenges:
- Requires disciplined adherence to technical practices.
4. Lean
Overview: Derived from Lean Manufacturing, this methodology emphasizes delivering value by eliminating waste and improving efficiency.
Best For: Teams aiming for value optimization and waste reduction.
Key Strengths:
Focuses on value streams and customer-centricity.
Encourages small batch delivery.
Challenges:
- May require significant process redesign.
5. Crystal
Overview: Crystal is a lightweight and customizable Agile framework, designed to adapt to team size, project criticality, and priorities.
Best For: Teams needing a tailored, minimalistic approach.
Key Strengths:
Flexibility in implementation.
Focus on communication and simplicity.
Challenges:
- Lack of structure can be problematic for larger teams.
6. Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM)
Overview: DSDM is a business-focused Agile framework prioritizing delivering projects on time and within budget while adjusting scope as needed.
Best For: Teams working on business-critical projects.
Key Strengths:
Clear focus on business value.
Strong governance structure.
Challenges:
- Heavy reliance on stakeholder involvement.
7. Feature-Driven Development (FDD)
Overview: FDD is a model-driven Agile methodology emphasizing iterative feature delivery.
Best For: Large-scale software projects.
Key Strengths:
Provides clear structure for large teams.
Focuses on delivering customer-valued features.
Challenges:
- Relatively rigid compared to other Agile methods.
8. Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe)
Overview: SAFe is designed for scaling Agile across large enterprises, coordinating multiple teams and complex projects.
Best For: Enterprises managing large-scale Agile initiatives.
Key Strengths:
Provides alignment across teams and portfolios.
Emphasizes continuous delivery at scale.
Challenges:
- Can feel bureaucratic if not implemented carefully.
9. Hybrid Agile
Overview: Hybrid Agile combines Agile practices with traditional approaches (e.g., Agile + Waterfall = “Water-Agile-Fall”).
Best For: Organizations transitioning to Agile or managing diverse projects with mixed requirements.
Key Strengths:
Flexibility to adapt to organizational needs.
Balances predictability and adaptability.
Challenges:
- Can dilute Agile principles if not carefully managed.